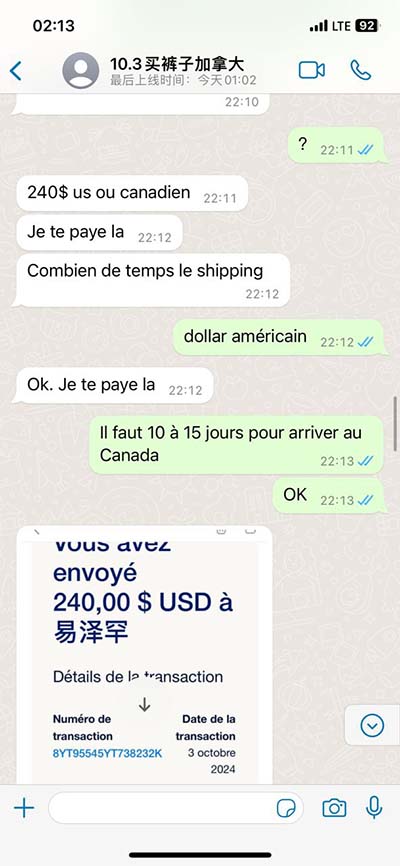
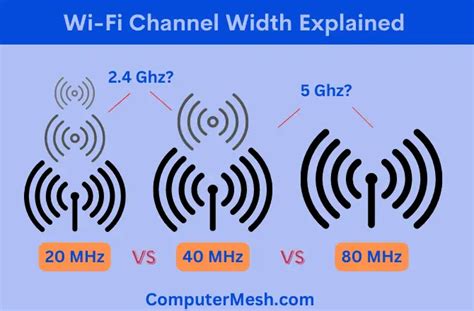
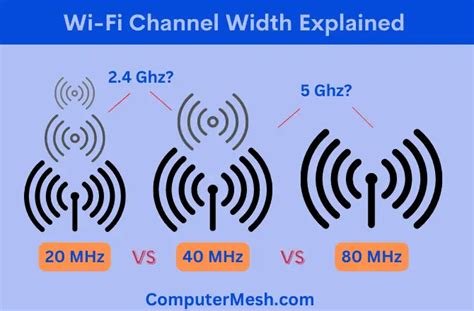
chanel width 20 or 40 | 2.4ghz bandwidth 20 or 40 chanel width 20 or 40 In the 2.4 GHz frequency, the Wi-Fi signal range is divided into channels each at 5 MHz interval. Adjacent channels overlap and will interfere with each other at 20 MHz block. . 142 Likes, 3 Comments - ELNELLA (@elnella.lv) on Instagram: “ElNella at the #MegaMillenialBall @elmomagalona @superjanella - @🎥: © @insideshowbiz - #ElNella.”
0 · wifi channel width 20 vs 40
1 · wifi 20hz vs 40hz
2 · what is bandwidth 20mhz 40mhz
3 · channel bandwidth 20 40 or
4 · 2.4ghz bandwidth 20 or 40
5 · 2.4ghz 20 or 40 mhz
6 · 2.4 channel bandwidth 20 40
7 · 11n bandwidth 20 or 40
Latvia. 57 followers 53 connections. Elinci. Latvijas Universitate. Personal site. Experience. Founder. Elinci. Oct 2013 - Present9 years 11 months. Decorating weddings and other festive.
The best channel width in the 5 GHz bands depends upon the number of active network devices. If there’s congestion, use a 20 MHz channel width; however, if there are . When it comes to selecting the right Wi-Fi channel width, every situation is different. By understanding the fundamentals, you can more effectively select a configuration that works . In the 2.4 GHz frequency, the Wi-Fi signal range is divided into channels each at 5 MHz interval. Adjacent channels overlap and will interfere with each other at 20 MHz block. . Set 5 GHz WiFi channel width to 20, 40, or 80 MHz. Wider WiFi channel widths— including 40 MHz and 80 MHz— are best used in the 5 GHz frequency band. In this band, .
wifi channel width 20 vs 40
wifi 20hz vs 40hz
40- (and 80-) MHz-wide channels are fine in the spacious 5GHz band. But 40MHz-wide channels can cause problems in the relatively narrow 2.4GHz band, where 40MHz wide . In the quest for the fastest and most reliable Wi-Fi, understanding bandwidth settings – specifically, the difference between 20, 40, 80, or 160 MHz channels “widths” – is .There are three common channel widths used in WiFi networks: 20 MHz: This is the standard channel width for most WiFi networks, both in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. A 20 MHz .
The standard width of a channel is 20 MHz. Bonding multiple 20 MHz channels together (to achieve 40/80/160 MHz) can increase throughput. But it’s only worth it if it doesn’t increase .
20 MHz is the standard channel width for most Wi-Fi networks, including the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. 20 MHz channel width provides a balance between data rate and stability. . When to Use 20mhz vs 40mhz vs 80mhz. Improving and managing Wi-Fi performance is important to everyone, from home users to large enterprises. Channel width plays a big role in Wi-Fi performance. Selecting the right width can have a huge impact. Getting it right isn't always straightforward, though. The best channel width in the 5 GHz bands depends upon the number of active network devices. If there’s congestion, use a 20 MHz channel width; however, if there are lesser chances of interference, use 40 or 80 MHz, or even 160 MHz for faster speeds.
ios app voor michael kors
what is bandwidth 20mhz 40mhz
jet set dressy tote michael kors
When it comes to selecting the right Wi-Fi channel width, every situation is different. By understanding the fundamentals, you can more effectively select a configuration that works best for you. While there is no one-size-fits all answer to the “20 MHz, 40 MHz, or 80 MHz?” question. In the 2.4 GHz frequency, the Wi-Fi signal range is divided into channels each at 5 MHz interval. Adjacent channels overlap and will interfere with each other at 20 MHz block. Setting the channel width to 40 MHz network will allow you to use 2/3 of the entire Wi-Fi band. Set 5 GHz WiFi channel width to 20, 40, or 80 MHz. Wider WiFi channel widths— including 40 MHz and 80 MHz— are best used in the 5 GHz frequency band. In this band, there are not only significantly more WiFi channels, but also less . 40- (and 80-) MHz-wide channels are fine in the spacious 5GHz band. But 40MHz-wide channels can cause problems in the relatively narrow 2.4GHz band, where 40MHz wide channels take up half the band and don't leave enough room for Bluetooth and other 2.4GHz technologies to work well.
In the quest for the fastest and most reliable Wi-Fi, understanding bandwidth settings – specifically, the difference between 20, 40, 80, or 160 MHz channels “widths” – is key. These settings can significantly impact your Wi-Fi performance, especially in .
There are three common channel widths used in WiFi networks: 20 MHz: This is the standard channel width for most WiFi networks, both in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. A 20 MHz channel width provides a balance between data transfer rates and the potential for interference.The standard width of a channel is 20 MHz. Bonding multiple 20 MHz channels together (to achieve 40/80/160 MHz) can increase throughput. But it’s only worth it if it doesn’t increase interference. After much testing, we recommend letting . 20 MHz is the standard channel width for most Wi-Fi networks, including the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. 20 MHz channel width provides a balance between data rate and stability. In the 802.11n protocol, the High Throughput (HT) Channel is defined. HT40 allows two 20 MHz channels to be bound to a single 40 MHz channel to increase wireless throughput.
When to Use 20mhz vs 40mhz vs 80mhz. Improving and managing Wi-Fi performance is important to everyone, from home users to large enterprises. Channel width plays a big role in Wi-Fi performance. Selecting the right width can have a huge impact. Getting it right isn't always straightforward, though. The best channel width in the 5 GHz bands depends upon the number of active network devices. If there’s congestion, use a 20 MHz channel width; however, if there are lesser chances of interference, use 40 or 80 MHz, or even 160 MHz for faster speeds.When it comes to selecting the right Wi-Fi channel width, every situation is different. By understanding the fundamentals, you can more effectively select a configuration that works best for you. While there is no one-size-fits all answer to the “20 MHz, 40 MHz, or 80 MHz?” question.
channel bandwidth 20 40 or
In the 2.4 GHz frequency, the Wi-Fi signal range is divided into channels each at 5 MHz interval. Adjacent channels overlap and will interfere with each other at 20 MHz block. Setting the channel width to 40 MHz network will allow you to use 2/3 of the entire Wi-Fi band.
Set 5 GHz WiFi channel width to 20, 40, or 80 MHz. Wider WiFi channel widths— including 40 MHz and 80 MHz— are best used in the 5 GHz frequency band. In this band, there are not only significantly more WiFi channels, but also less .
40- (and 80-) MHz-wide channels are fine in the spacious 5GHz band. But 40MHz-wide channels can cause problems in the relatively narrow 2.4GHz band, where 40MHz wide channels take up half the band and don't leave enough room for Bluetooth and other 2.4GHz technologies to work well.
In the quest for the fastest and most reliable Wi-Fi, understanding bandwidth settings – specifically, the difference between 20, 40, 80, or 160 MHz channels “widths” – is key. These settings can significantly impact your Wi-Fi performance, especially in .There are three common channel widths used in WiFi networks: 20 MHz: This is the standard channel width for most WiFi networks, both in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. A 20 MHz channel width provides a balance between data transfer rates and the potential for interference.The standard width of a channel is 20 MHz. Bonding multiple 20 MHz channels together (to achieve 40/80/160 MHz) can increase throughput. But it’s only worth it if it doesn’t increase interference. After much testing, we recommend letting .
iphone hoesje 6s michael kors
Office locations. Everything you need to contact us for insurance product information in one place. How to make a claim, change your details, access your account and FAQs.
chanel width 20 or 40|2.4ghz bandwidth 20 or 40