lv dp/dt max | global left ventricular systolic function lv dp/dt max Normal Vp is 50 cm/s and correlates with the rate of myocardial relaxation. However, Vp can be increased in patients with normal LV volumes and EFs, despite impaired relax-ation. . 1.3K. 343K views 10 years ago. 5 steps on how to tell if your Louis Vuitton Belt is authentic and what it looks like on with formal and casual attire. This episode we have the Louis.
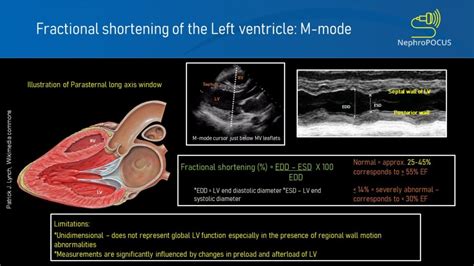
0 · lv fractional shortening
1 · lv dp dt normal values
2 · lv dp dt echo
3 · left ventricular function assessment
4 · left ventricular fractional shortening
5 · left ventricular diastolic function indeterminate
6 · how to assess lv function
7 · global left ventricular systolic function
Compared to an authentic belt, the “LV” buckle on a fake is often rounded, not straight, not as sharply or finely cut, and too thick or thin. [1] Look at the buckle’s color, too. The “LV” logo might be duller than a real “LV” logo and the hue may look off. For instance, a fake gold “LV” logo might be too brassy.
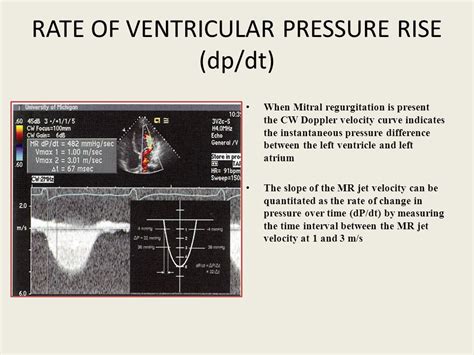
dP/dt. In the setting of mitral regurgitation, left ventricular systolic function can be estimated by studying the acceleration of the regurgitant jet (Figure 2). The better the systolic function, the greater the increase in left ventricular systolic pressure, and, thus, the greater the acceleration .Stroke volume (SV) is the volume of blood ejected by the right/left ventricle in a single contraction. It is the difference between the end-diastolic volume (EDV) and the end-systolic volume (ESV). In mathematical terms, The stroke volume is affected by changes in preload, afterload, and inotropy (.The value of 117% is equivalent to 2 s.d. from the upper normal limit corrected to age and BSA plus 5%. For the purposes of this guideline, it is recommended that a value above 2 s.d. s for .Normal Vp is 50 cm/s and correlates with the rate of myocardial relaxation. However, Vp can be increased in patients with normal LV volumes and EFs, despite impaired relax-ation. .
LV dP/dt max was assessed using continuous-wave Doppler analysis of mitral regurgitation flow. Results. Values from continual arterial dP/dt max monitoring were .We compared LV and arterial (femoral and radial) dP/dt max to the slope of the LV end-systolic pressure-volume relationship (Ees), a load-independent measure of LV contractility, to .
Key points. Left ventricular (LV) dP/dt max is measured invasively using a pressure-wire or pressure-volume catheter in the LV and provides a sensitive measure of the acute hemodynamic response to cardiac . We compared LV and arterial (femoral and radial) dP/dt max to the slope of the LV end-systolic pressure-volume relationship (Ees), a load-independent measure of LV .
LV dP/dt max is used to determine acute response to CRT to secure long-term benefits from CRT. This study shows that LV dP/dt max is not determined by optimal . LV dP/dt max was assessed using continuous-wave Doppler analysis of mitral regurgitation flow. Results. Values from continual arterial dP/dt max monitoring were .dP/dt. In the setting of mitral regurgitation, left ventricular systolic function can be estimated by studying the acceleration of the regurgitant jet (Figure 2). The better the systolic function, the greater the increase in left ventricular systolic pressure, and, thus, the greater the acceleration in the regurgitant jet.
An increase in contractility is manifested as an increase in dP/dt max during isovolumic contraction. However, dP/dt max is also influenced by preload, afterload, heart rate, and myocardial hypertrophy.The value of 117% is equivalent to 2 s.d. from the upper normal limit corrected to age and BSA plus 5%. For the purposes of this guideline, it is recommended that a value above 2 s.d. s for age, sex and BSA should be used in diagnosis, using linear .Normal Vp is 50 cm/s and correlates with the rate of myocardial relaxation. However, Vp can be increased in patients with normal LV volumes and EFs, despite impaired relax-ation. Therefore, Vp is most reliable as an index of LV relaxation in patients with .
LV dP/dt max was assessed using continuous-wave Doppler analysis of mitral regurgitation flow. Results. Values from continual arterial dP/dt max monitoring were significantly correlated with LV dP/dt max assessed using echocardiography (r = 0.70 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.51–0.82]; P < 0.0001).We compared LV and arterial (femoral and radial) dP/dt max to the slope of the LV end-systolic pressure-volume relationship (Ees), a load-independent measure of LV contractility, to determine the interactions between dP/dt max and Ees as loading and LV contractility varied.
Key points. Left ventricular (LV) dP/dt max is measured invasively using a pressure-wire or pressure-volume catheter in the LV and provides a sensitive measure of the acute hemodynamic response to cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT).
We compared LV and arterial (femoral and radial) dP/dt max to the slope of the LV end-systolic pressure-volume relationship (Ees), a load-independent measure of LV contractility, to determine the interactions between dP/dt max and Ees as loading and LV contractility varied. LV dP/dt max is used to determine acute response to CRT to secure long-term benefits from CRT. This study shows that LV dP/dt max is not determined by optimal resynchronisation but rather by LV pre-excitation in patients amenable for CRT and will not be useful as a biomarker for CRT. LV dP/dt max was assessed using continuous-wave Doppler analysis of mitral regurgitation flow. Results. Values from continual arterial dP/dt max monitoring were significantly correlated with LV dP/dt max assessed using echocardiography (r = 0.70 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.51–0.82]; P < 0.0001).
lv fractional shortening
dP/dt. In the setting of mitral regurgitation, left ventricular systolic function can be estimated by studying the acceleration of the regurgitant jet (Figure 2). The better the systolic function, the greater the increase in left ventricular systolic pressure, and, thus, the greater the acceleration in the regurgitant jet.
An increase in contractility is manifested as an increase in dP/dt max during isovolumic contraction. However, dP/dt max is also influenced by preload, afterload, heart rate, and myocardial hypertrophy.The value of 117% is equivalent to 2 s.d. from the upper normal limit corrected to age and BSA plus 5%. For the purposes of this guideline, it is recommended that a value above 2 s.d. s for age, sex and BSA should be used in diagnosis, using linear .Normal Vp is 50 cm/s and correlates with the rate of myocardial relaxation. However, Vp can be increased in patients with normal LV volumes and EFs, despite impaired relax-ation. Therefore, Vp is most reliable as an index of LV relaxation in patients with .
LV dP/dt max was assessed using continuous-wave Doppler analysis of mitral regurgitation flow. Results. Values from continual arterial dP/dt max monitoring were significantly correlated with LV dP/dt max assessed using echocardiography (r = 0.70 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.51–0.82]; P < 0.0001).
We compared LV and arterial (femoral and radial) dP/dt max to the slope of the LV end-systolic pressure-volume relationship (Ees), a load-independent measure of LV contractility, to determine the interactions between dP/dt max and Ees as loading and LV contractility varied. Key points. Left ventricular (LV) dP/dt max is measured invasively using a pressure-wire or pressure-volume catheter in the LV and provides a sensitive measure of the acute hemodynamic response to cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). We compared LV and arterial (femoral and radial) dP/dt max to the slope of the LV end-systolic pressure-volume relationship (Ees), a load-independent measure of LV contractility, to determine the interactions between dP/dt max and Ees as loading and LV contractility varied. LV dP/dt max is used to determine acute response to CRT to secure long-term benefits from CRT. This study shows that LV dP/dt max is not determined by optimal resynchronisation but rather by LV pre-excitation in patients amenable for CRT and will not be useful as a biomarker for CRT.
lv dp dt normal values

The LV Initials 40mm Matte Black Belt brings effortless elegance to everyday ensembles. This permanent House style is updated with a matte lacquer finish on the LV buckle for a modern look. A highly wearable piece, it is immaculately crafted from Monogram Eclipse canvas and plain calf leather.
lv dp/dt max|global left ventricular systolic function